Webhooks
Webhooks allow external applications to receive real-time notifications when specific events occur in the Babel Licensing Service. This feature enables seamless integration with your existing systems, allowing you to automate workflows and keep your data synchronized.
Webhooks
Accessing Webhooks
Webhooks are available from the main navigation menu in the Babel Licensing Service. Click on the “Webhooks” menu item in the left sidebar to access the webhooks management interface.
Managing Webhooks
Viewing Webhooks
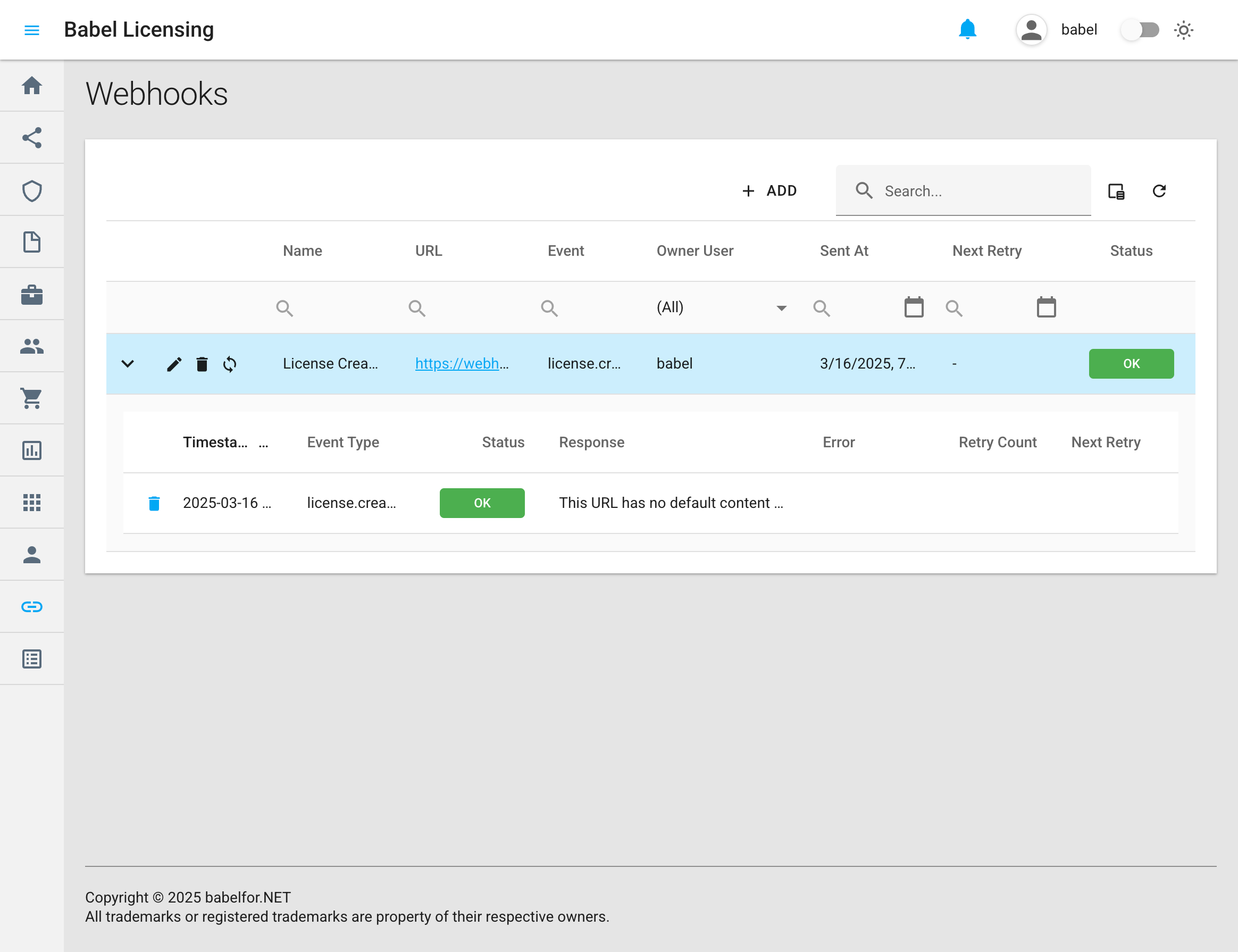
The webhooks page displays a table with all configured webhook subscriptions and their details:
- Name: A descriptive name for the webhook
- URL: The endpoint where event notifications will be sent
- Event: The type of event the webhook is subscribed to
- Owner User: The user who created the webhook
- Sent At: The timestamp of the last event delivery
- Next Retry: When the next delivery attempt will occur (if applicable)
- Status: Current status of the webhook (OK, Error, etc.)
Adding a New Webhook
To create a new webhook subscription:
- Click the ”+ ADD” button in the top-right corner of the webhooks page
- Fill in the required information:
- Name: Enter a descriptive name for the webhook
- URL: Provide the endpoint URL where notifications should be sent
- Event: Select the event type(s) you want to subscribe to
- Secret: Generate or enter a secret key for request verification
- Click “Save” to create the webhook subscription
Editing a Webhook
To edit an existing webhook subscription:
- Find the webhook in the list
- Click the edit icon (pencil) in the row
- Modify the webhook details
- Click “Save” to update the webhook subscription
Deleting a Webhook
To delete a webhook subscription:
- Find the webhook subscription in the list
- Click the delete icon (trash) in the row
- Confirm the deletion when prompted
Testing a Webhook
To test a webhook subscription:
- Find the webhook subscription in the list
- Click the refresh icon to send a test event
- View the delivery result in the webhook events details
The system will process the test event through the same delivery mechanism as real events, including the same headers and signature verification, allowing you to validate your endpoint’s handling of webhook payloads.
Webhook Event Details
When a webhook is triggered, the expanded view shows delivery details:
- Timestamp: When the event occurred
- Event Type: The type of event (e.g., license.created)
- Status: Delivery status (OK, Failed)
- Response: The response received from your endpoint
- Error: Any error messages (if delivery failed)
- Retry Count: Number of delivery attempts
- Next Retry: When the next retry will occur (if applicable)
Supported Events
Babel Licensing Service supports the following webhook events:
Licenses
- license.created Triggered when a new license is created.
- license.updated Triggered when an existing license is updated.
- license.deleted Triggered when a license is deleted.
- license.expiring Triggered when a license is about to expire.
- license.expired Triggered when a license has expired.
- license.revoked Triggered when a license is revoked.
- license.supportexpiring Triggered when a license’s support is about to expire.
- license.supportexpired Triggered when a license’s support has expired.
- license.activated Triggered when a license is activated.
- license.deactivated Triggered when a license is deactivated.
- license.requested Triggered when a license is requested.
- license.released Triggered when a license is released.
Orders
- order.created Triggered when a new order is created.
- order.updated Triggered when an existing order is updated.
- order.deleted Triggered when an order is deleted.
Reports
report.created Triggered when a new report is created.
Webhook Payload Reference
This section provides detailed information about the structure and content of webhook event payloads for different event types.
License Event Payload
When handling a license event (like license.created), the payload includes the following fields:
{
"Id": 101,
"LicenseId": "LIC-0001",
"UserKey": "XJK-SHJD-GE5E",
"Licensee": "Acme Corp",
"LicensingMode": "Activation",
"IssueDate": "2025-03-16T00:00:00Z",
"SupportExpireDate": "2026-03-16T00:00:00Z",
"ExpireDate": "2025-12-31T23:59:59Z",
"CustomerId": 501,
"OrderId": 302,
"TemplateId": 10,
"Revoked": false,
"Trace": "trace_info",
"EventType": "license.created",
"Timestamp": "2025-03-16T12:00:00Z"
}| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
Id | Integer | The unique database identifier for the license. Used for API reference and internal tracking. |
LicenseId | String | A human-readable license identifier (e.g., "LIC-0001") used in customer communications and documentation. |
UserKey | String | The activation key that end-users enter to activate the licensed software. |
Licensee | String | The name of the individual or organization to whom the license is issued. |
LicensingMode | Integer | The type of licensing mode applied (e.g., "0: File", "1: Activation", "2: Floating"). |
IssueDate | ISO 8601 DateTime | The date and time when the license was initially issued. |
SupportExpireDate | ISO 8601 DateTime | The date and time when technical support for this license ends. |
ExpireDate | ISO 8601 DateTime | The date and time when the license itself expires and becomes invalid. |
CustomerId | Integer | Reference to the customer who owns this license. Maps to a customer record in the system. |
OrderId | Integer | Reference to the order through which this license was purchased. |
TemplateId | Integer | The ID of the license template used to generate this license, determining its features and limitations. |
Revoked | Boolean | Indicates whether the license has been invalidated administratively (true) or remains active (false). |
Trace | Boolean | Indicates whether the license has tracing enabled. |
EventType | String | Identifies the specific event type that triggered this webhook (e.g., "license.created", "license.updated"). |
Timestamp | ISO 8601 DateTime | The exact time when the event occurred and the webhook was dispatched. |
Order Event Payload
For order-related events (like order.created), the webhook payload contains these fields:
{
"Id": 202,
"OrderNumber": "ORD-12345",
"CustomerId": 501,
"CreatedAt": "2025-03-16T12:00:00Z",
"Status": "completed",
"EventType": "order.created",
"Timestamp": "2025-03-16T12:05:00Z"
}| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
Id | Integer | The unique database identifier for the order. Use this ID when making API calls for order details. |
OrderNumber | String | A human-readable order reference number used in customer communications and financial records. |
CustomerId | Integer | The unique identifier of the customer who placed the order. References a customer record. |
CreatedAt | ISO 8601 DateTime | The date and time when the order was initially created in the system. |
Status | String | The current processing status of the order. Possible values include: "pending", "processing", "completed", "cancelled", "refunded". |
EventType | String | Identifies which order event triggered this webhook (e.g., "order.created", "order.updated", "order.deleted"). |
Timestamp | ISO 8601 DateTime | The exact time when the event occurred and the webhook was dispatched. |
Report Event Payload
For report-related events (like report.created), the webhook payload includes these fields:
{
"Id": 303,
"Name": "Monthly Report",
"Date": "2025-03-15T00:00:00Z",
"EventType": "report.created",
"Timestamp": "2025-03-16T12:10:00Z"
}| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
Id | Integer | The unique database identifier for the report. Use this ID to retrieve the full report via API. |
Name | String | The descriptive title of the report as defined in the system. |
Date | ISO 8601 DateTime | The date associated with the report content (typically the reporting period end date). |
EventType | String | Identifies which report event triggered this webhook (currently only "report.created"). |
Timestamp | ISO 8601 DateTime | The exact time when the event occurred and the webhook was dispatched. |
Webhook Delivery and Retry Logic
Babel Licensing Service processes webhooks through a background service that runs continuously:
- The service checks for new webhook events every 30 seconds
- Webhooks are processed in batches of up to 50 events at a time
- The system handles both pending (new) events and previously failed events that are scheduled for retry
- Each webhook delivery includes standard headers:
User-Agent: Identifies the Babel Licensing ServiceX-Babel-Webhook-Id: Unique identifier for the webhook deliveryX-Babel-Event: The type of event being deliveredX-Babel-Timestamp: When the event was dispatchedX-Babel-Signature: HMAC-SHA256 signature (if a secret is configured)
Retry Mechanism
When a webhook delivery fails:
- The system automatically schedules a retry for 5 minutes later
- Each webhook can be configured with a maximum retry count
- Failed events remain in the system until they are successfully delivered or the maximum retry count is reached
- The webhook interface shows the next scheduled retry time for failed deliveries
- Each failed delivery stores the error message or HTTP status code for troubleshooting
Webhook Status
Webhooks in the system can have the following statuses:
- OK: Event was successfully delivered
- Failed: Event delivery failed and maximum retries were exceeded
- Pending: Event is waiting to be processed
- Scheduled: Event delivery failed and is scheduled for retry
Securing Webhooks
All webhook requests include a signature in the X-Babel-Signature header. This signature is generated using HMAC-SHA256 with your webhook’s secret key and the request body as input.
To verify the webhook:
- Get the signature from the
X-Babel-Signatureheader - Compute an HMAC-SHA256 signature using your secret key and the raw request body
- Compare the computed signature with the one in the header
- Only process the webhook if signatures match
Example verification code (C#):
private bool VerifyWebhookSignature(string payload, string signatureHeader, string secret)
{
using var hmac = new HMACSHA256(Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(secret));
var computedHash = hmac.ComputeHash(Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(payload));
var computedSignature = Convert.ToBase64String(computedHash);
return signatureHeader == computedSignature;
}Implementing a Webhook Receiver
Below is a complete example of how to implement a webhook receiver in ASP.NET Core that properly validates webhook signatures:
// WebhookValidator.cs
using System;
using System.Security.Cryptography;
using System.Text;
namespace YourProject.Utilities
{
public static class WebhookValidator
{
/// <summary>
/// Validates the webhook payload against the provided signature using HMAC-SHA256.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="payload">The raw JSON payload.</param>
/// <param name="secret">The shared secret.</param>
/// <param name="signature">The signature from the incoming request header.</param>
/// <returns>True if the signature is valid; otherwise, false.</returns>
public static bool ValidateSignature(string payload, string secret, string signature)
{
using var hmac = new HMACSHA256(Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(secret));
var hash = hmac.ComputeHash(Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(payload));
var computedSignature = BitConverter.ToString(hash).Replace("-", "").ToLowerInvariant();
return string.Equals(computedSignature, signature, StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase);
}
}
}
// WebhookController.cs
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging;
using System.IO;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using YourProject.Utilities;
namespace YourProject.Controllers
{
[ApiController]
[Route("api/webhook")]
public class WebhookController : ControllerBase
{
private readonly ILogger<WebhookController> _logger;
// Ideally, the secret comes from configuration
private readonly string _webhookSecret = "your-webhook-secret";
public WebhookController(ILogger<WebhookController> logger)
{
_logger = logger;
}
[HttpPost]
public async Task<IActionResult> ReceiveWebhook()
{
// Read the payload from the request body
var payload = await new StreamReader(Request.Body).ReadToEndAsync();
// Retrieve the signature from the request headers
if (!Request.Headers.TryGetValue("X-Babel-Signature", out var incomingSignature))
{
_logger.LogWarning("Missing X-Babel-Signature header");
return Unauthorized("Signature header missing");
}
// Validate the signature
if (!WebhookValidator.ValidateSignature(payload, _webhookSecret, incomingSignature))
{
_logger.LogWarning("Invalid webhook signature");
return Unauthorized("Invalid signature");
}
// Process the webhook payload
_logger.LogInformation("Webhook payload validated and processed");
// TODO: Deserialize and process the payload as needed
return Ok();
}
}
}Best Practices for Receiving Webhooks
When implementing a webhook receiver:
- Always validate signatures - Use the provided signature validation code to verify the authenticity of each webhook
- Store your webhook secret securely - Don’t hardcode it as shown in the example; use a secure configuration system
- Respond quickly - Return a 200 OK response as soon as you’ve validated the signature
- Process asynchronously - After validating and returning a response, process the webhook in a background thread or queue
- Implement idempotency - Use the event ID to avoid processing duplicate webhooks if they’re delivered more than once
- Log all webhook events - Keep a record of all received webhooks for debugging and auditing
Processing Webhook Events
Handling Different Event Types
Your webhook receiver should be designed to handle different event types appropriately. Here’s an example of how you might process various webhook events after validating the signature:
// Example of webhook event processing
private async Task ProcessWebhookEvent(string payload, string eventType)
{
switch (eventType)
{
case "license.created":
await ProcessNewLicense(payload);
break;
case "license.expired":
await ProcessExpiredLicense(payload);
break;
case "order.created":
await ProcessNewOrder(payload);
break;
// Handle other event types
default:
_logger.LogWarning($"Unhandled webhook event type: {eventType}");
break;
}
}
// Example deserialization and processing
private async Task ProcessNewLicense(string payload)
{
try
{
// Deserialize the payload
var licenseEvent = JsonSerializer.Deserialize<LicenseCreatedEvent>(payload);
// Process the license
_logger.LogInformation($"Processing new license: {licenseEvent.LicenseId}");
// Example: Store in your database, notify users, etc.
await _licenseService.SyncLicenseAsync(licenseEvent.Id);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
_logger.LogError(ex, "Error processing license.created webhook");
}
}Troubleshooting
Common Issues
- Webhook not receiving events: Check the webhook status in the dashboard and verify the event type is one you’ve subscribed to
- Authentication failures: Verify your signature validation code is correct and that you’re using the same secret as configured in the webhook
- Timeouts: Ensure your endpoint responds within a reasonable time (the system waits for a response before marking as successful)
- Invalid URL: Check that your webhook URL is accessible from the internet and returns HTTP 2xx status codes
- Custom headers not being applied: Review the format of your custom headers in the webhook configuration
- Webhook marked as failed: Check the error message in the webhook details to see the specific HTTP status code or exception that occurred
Viewing Webhook History
For each webhook, you can view the complete delivery history:
- Click on a webhook in the main list to expand its details
- The history section shows all delivery attempts with timestamps, event types, status, and any error messages
- Use this information to diagnose delivery issues or verify successful deliveries